Lecture 2 (3/30/22)¶
Getting back in the swing of things…
Datahub and jupyter notebooks
Python review: operations + data types

First up: jupyter notebooks¶
This is a “markdown” cell!
You can format markdown cells in lots of ways:
BIIIIGGG HEADERS¶
Medium Headers¶
smol headers¶
extra smol headers??¶
extra smol italic headers???¶
You can also format regular text:
FORTUNE favors the BOLD.
Markdown is powerful, but it will never be:
bullet
proof
Indeed, some would say markdown’s:
days
are
numbered
A few other tricks:
You can add hyperlinks to the World Wide Web
You can also embed images:
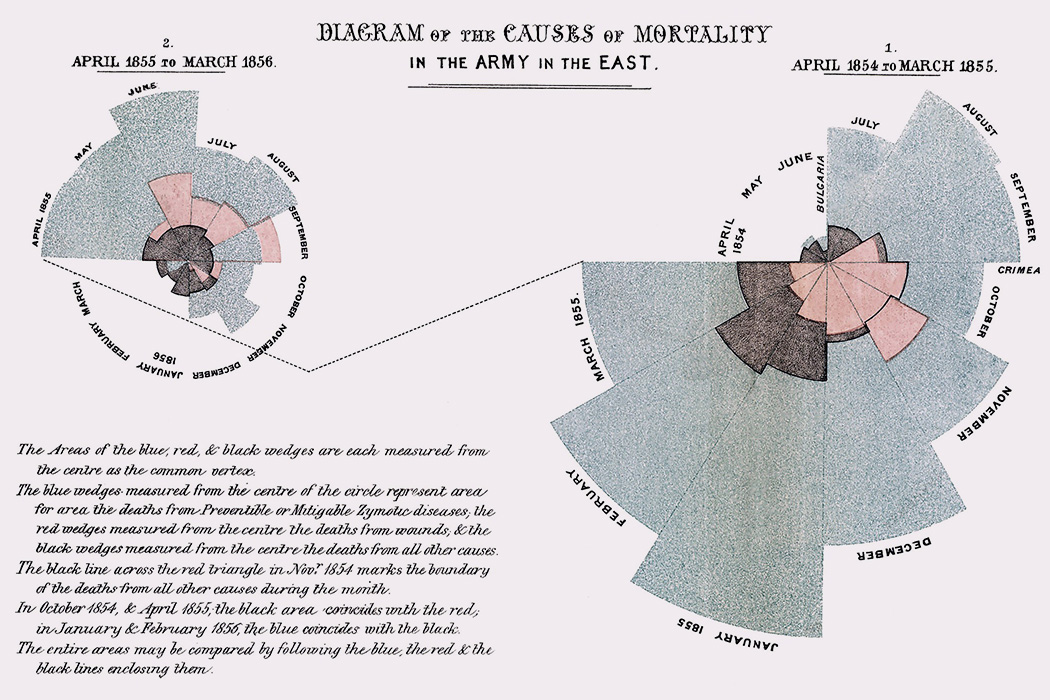
In fact, markdown essentially compiles to HTML, so if you have experience coding in HTML, you can do all kinds of nifty things.
Hello, world.
What’s the point of markdown cells anyway?¶
Good question! Jupyter notebooks are made to simplify the process of sharing and collaborating with code.
Often, it’s helpful to annotate what your code is doing, describe results in more detail, or just organize your code into different sections.
Markdown cells give you the tools to do that.
…But what about the code? 🤖 🤖 🤖 🤖 🤖
# You can also run python code in jupyter notebooks!
# That's actually their main job!
print("hello, world")
hello, world
So what kind of code will we run?
Time for… python review!¶
The goal of this section is to refresh your memory for the basics of python coding.
This should be a review for most of you!
However, the more practice you get with the python basics, the easier everything else this quarter will be.
If you have questions about any of this, it’s important to clear them up now :)
Operations¶
# Arithmetic
# Booleans ('and', 'or', 'not')
# Comparison (>, <, ==, !=)
# Assignment
# bonus: assignment shorthand (+=)
# Special operation: 'in'
Data types¶
Integers and floats¶
# Integers and floats
# Operations: math!
Strings¶
# Strings
foo = ''
bar = ""
# Operations
find()
replace()
split()
# bonus: string indexing
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NameError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-9-4b946496cb45> in <module>
6
7 # Operations
----> 8 find()
9 replace()
10 split()
NameError: name 'find' is not defined
Identifying data types and operations¶
A rose by any other name…
foo = "bar"
print(type(foo)) # What kind of thing is this?
print(dir(foo)) # What operations can we do with this?
# Casting
<class 'str'>
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isascii', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill']
Data structures¶
Lists¶
What is a list?
# Declaring lists
foo = ['bar']
# Adding and removing items
append()
extend()
insert()
remove()
# Accessing items: indexing, 'in'
# bonus: len
# Operations: sort, reverse
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NameError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-11-e7367cf99e8a> in <module>
6
7 # Adding and removing items
----> 8 append()
9 extend()
10 insert()
NameError: name 'append' is not defined
Dictionaries¶
What is a dictionary?
# Declaring dictionaries
foo = {}
foo = dict()
# Adding and removing items
# Accessing items
# bonus: 'keys', 'values', 'items'
Sets¶
What is a set?
# Declaring sets
foo = set()
foo = set('hi how are you')
bar = set('doing fine')
foo = {1, 2, 3, 4}
bar = {2}
# Adding and removing items
# Set operations: &, -, |
# Accessing items: bit tricky...
